no photo available
Lucas Bull was one of the founders of the Durban Chess Club in
1893 and the first person to win the Durban championship on five
occasions, running out the winner in 1901, 1903, 1904, 1906 and 1911.
He also participated in the South African championships on three occasions,
finishing 9th in 1897, 7th in 1899, and 2nd on his final appearance in 1906.
Lucas Bull was born in Twickenham (part of London) in 1869, and
came from a very large family, consisting of five sons (he was
the third son) and four daughters.
His father, Thomas Bull, was a surveyor and auctioneer, and must have
had a profitable business, as the Bull family employed four servants
at the time (source: 1881 census).
Bull arrived in Durban in 1892 and apparently chose South Africa,
rather than the United States, as they don't play cricket in the USA!
He was already the champion of the Twickenham Chess Club, and was
starting to get an international reputation as a problemist. From
the date of his arrival, up until the time that he discontinued
serious over the board play in 1907, he was almost certainly the
strongest player in Natal.
Lucas Bull is world famous as a composer of chess problems. He
wrote a column on chess for the "Natal Advertiser" (now
better known as the "Daily News") from 1893 to 1907 where
he published many of his problems. The chess column in the "Natal
Advertiser" stopped publishing problems in 1908 and thereafter
his problems appeared frequently in the "Natal Mercury".
A selection of his best 3 move mate problems can be seen in the book
"Sonatas in Chess" written by Donald McIntyre.
Here is a game from 1899 played in the South
African Championship (source: Len Reitstein).
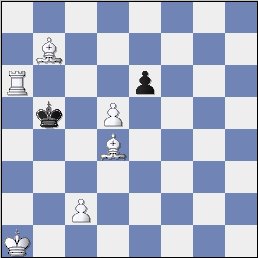
Problem Solution
1.Ra3! forces mate. This is a problem in the Bohemian
style which Bull specialised in. Notice that each square is
covered only once, and that the King is only attacked by one
piece at the end, making this a model mate. The nicest
line is probably 1.Ra3! Kb4 2.Bc6 Kxa3 3.Bc5 mate.
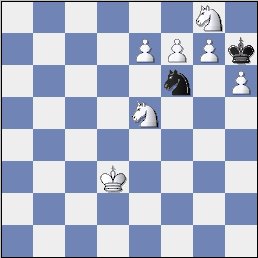
Problem Solution
The key move is an under promotion by 1.e8=N.
There are three main variations, namely 1...Nxg8 2.fxg8=N Kxg8 3.Nf6#
or 1...Nxe8 2.fxe8=N Kxg8 3.Nf6# or 1...Nd5 2.f8=N+ Kxg8 3.h7#